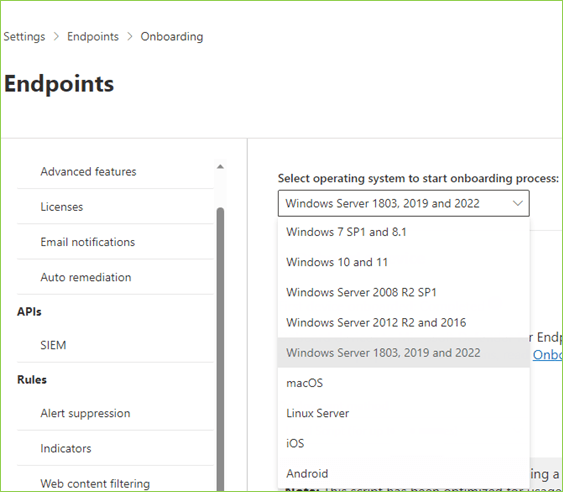
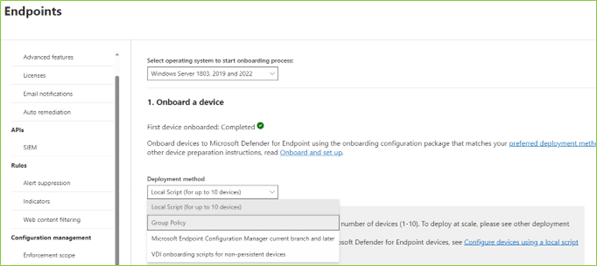
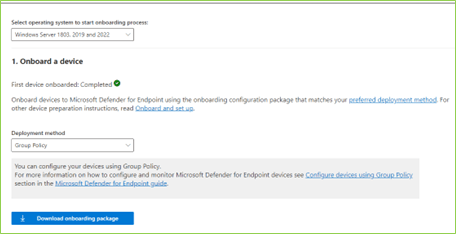
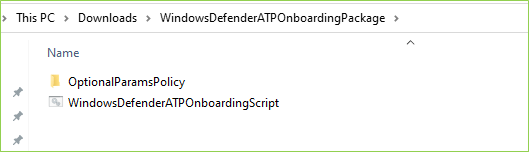
The Power of Imagination: A Beginner’s Guide to Generative AI
Overview
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a class of AI models and techniques designed to produce new, original data that imitates human-like creativity and imagination. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on pattern recognition and making decisions based on existing data, generative AI creates new content that didn’t exist in the training dataset. It is capable of generating various types of content, such as images, music, text, and even videos.
The underlying principle of generative AI lies in the use of deep learning models, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). GANs consist of two networks, a generator, and a discriminator, that play a game to produce increasingly realistic data. VAEs, on the other hand, work on the basis of encoding and decoding data to create representations in a latent space.
Benefits of Generative Artificial Intelligence
Generative AI finds application in various domains today:
- Content creation: Actively generate new content for purposes like news, marketing, or music. This is beneficial because it’s new, original, and tailored.
- Data augmentation: Augmenting data sets increases the size and diversity of data, which is useful for training models or deriving insights. This capability is crucial for machine learning, as it helps models learn from more data and avoid overfitting.
- Artificial creativity: Sparking creativity by actively creating new and original works of art, which may include paintings, sculptures, music, and poetry.
- Product design: Contributing to the design process of new products, businesses can leverage generative AI to create innovative and consumer-appealing products.
Examples of Generative Artificial Intelligence
As generative AI continues to develop, we witness even more innovative and creative applications for this technology in the fields of Music, Journalism, Video Games Development, Art, Healthcare and in almost all fields.
Here are some of the examples of its application:
- ChatGPT: A generative AI chatbot capable of generating realistic and engaging conversations. Trained on a massive dataset of text and code, it finds utility in customer service, education, and entertainment.
- DALL-E: A generative AI image creation tool, utilizing text descriptions to generate realistic and creative images, drawing from a vast dataset of images and text.
- Bard: Bard is a large language model from Google AI that can generate text and translate languages. It can also write different kinds of creative content and answer your questions in an informative way. It is still under development, but it has learned to perform many kinds of tasks.
Conclusion
Generative AI is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field with many potential benefits and challenges for society. It can enable new forms of creativity, innovation, education, entertainment, and communication. However, it can also pose ethical, legal, and social issues, such as privacy, security, authenticity, accountability, and fairness. Therefore, it is vital to understand the basics of generative AI, its applications, and its limitations and risks.